
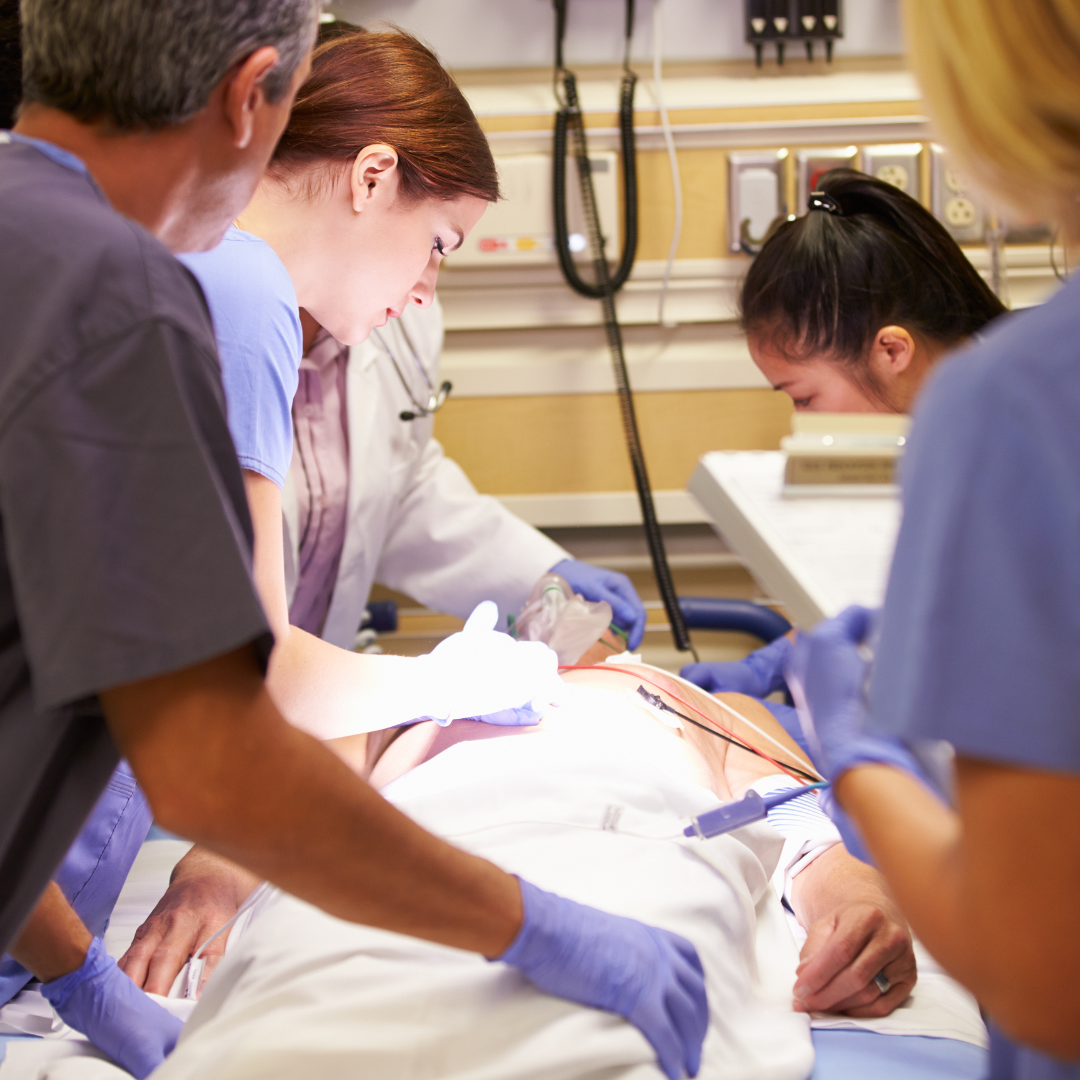
 EMERGENCY ROOM PHYSICIAN: An ER Physician provides primary care to the host of patients entering with illnesses and injuries covering a broad spectrum, from acute infections to life-threatening conditions. An ER physician must have comprehensive medical knowledge They must identify possible causes of the many symptoms a patient can present with and must be able to treat many conditions. ER physicians are not qualified or licensed to perform surgeries. ER physicians may request a consultation with a specialist, may stabilize a patient, or occasionally deliver a baby themselves.
EMERGENCY ROOM PHYSICIAN: An ER Physician provides primary care to the host of patients entering with illnesses and injuries covering a broad spectrum, from acute infections to life-threatening conditions. An ER physician must have comprehensive medical knowledge They must identify possible causes of the many symptoms a patient can present with and must be able to treat many conditions. ER physicians are not qualified or licensed to perform surgeries. ER physicians may request a consultation with a specialist, may stabilize a patient, or occasionally deliver a baby themselves.
Have you considered?
NURSING CAREERS IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE: Because every ER has limited resources and a set number of physicians and staff members present at any given time, the primary duty of an ER nursing staff is triage. This involves rapid evaluation of incoming patients— usually based upon chief complaints and prioritizing them based upon the likelihood a person has a severe illness.
EMT/PARAMEDIC: An EMT (short for Emergency Medical Technician) or paramedic is trained to administer this on-site emergency care. Upon arriving on the scene, he or she assesses the patient's injuries or illness, provides emergency treatment and then the EMT or paramedic transports the patient to a medical facility for further treatment. The duties of EMTs and paramedics often overlap, but paramedics are trained to deliver more advanced care than EMTs.

After completing 4 years of medical or osteopath school, a physician interested in practicing emergency medicine must complete an emergency medicine residency program. The residency provides comprehensive training. These programs are typically 3 years in length. An ER physician must hold a license by the state medical board to practice medicine in general. After completing the emergency medicine residency, the physician must pass a board-certification examination in emergency medicine in order to practice medicine in that specialty area.
There are three educational paths to becoming a nurse. A diploma from an accredited nursing program or hospital (CNA, LPN), an associate’s degree in nursing (ADN – a two-year program), or a bachelor’s degree (Bachelor of Science in Nursing, or BSN). Nurses are involved with nearly all aspects of a patient’s care. Schedules and duties vary based on the type and level of the nursing role. Nurses can be generalists or obtain Master’s degrees and additional certifications to specialize in many different areas of healthcare.
To work as an EMT or paramedic, you must be licensed. You must have a high school diploma before certifying to become an EMT or Paramedic. The biggest differences between paramedics and EMTs are the training and the scope of practice (what they are allowed to do). Basic EMTs usually receive 120 - 150 hours of training, while paramedics get anywhere from 1,200 hours to 1,800 hours of training. Paramedic programs often award two-year degrees.
US Earning Potential Averages For Emergency Medical Physicians: (Jobs.Utah.Gov)
|
Annual Total Openings: |
21,400 |
|---|---|
|
Annual Growth Rate: |
3% |
|
Median Annual Wage: |
$208,000 |
|
Education: |
Doctoral/Professional Degree |
Utah Earning Potential Averages For EMTs: (Jobs.Utah.Gov)
|
Annual Total Openings: |
170 |
|---|---|
|
Annual Growth Rate: |
2.2% |
|
Median Annual Wage: |
$74,970 |
|
Inexperienced Annual Wage: |
$53,443 |
|
Education: |
Post Secondary Certification, 2 yrs |


